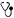Bladder Augmentation (Ileal or Ileocaecal)
Augmentation
The urinary bladder is an expandable balloon-like organ that receives urine from the kidneys and stores it until it can be conveniently expelled to the outside. Sometimes, the bladder is not big enough, or is too stiff and cannot completely expand to hold the normal amount of urine produced by the kidneys. If this condition is not treated, urine may leak from the bladder (incontinence) or back up towards the kidneys (reflux).
Augmentation is a procedure used to enlarge the bladder, lower the pressure created inside the bladder or enhance its ability to stretch in order to accommodate the complete volume of urine produced.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopic bladder augmentation, also called cystoplasty, is a surgical technique performed to increase the size of the bladder when the bladder is not big enough or is too stiff and cannot completely expand to hold the normal amount of urine produced by the kidneys. Cystoplasty is performed to treat urine leakage (incontinence) or reflux, where the urine backs up towards the kidneys. Laparoscopic bladder augmentation is performed under general anaesthesia. Your surgeon makes 3 to 4 small keyhole incisions on the abdomen. A laparoscope (tube with a light and a small camera) is inserted to view the abdominal cavity. Your surgeon inserts surgical instruments to make an incision on the top of the bladder. A piece of the intestine or stomach is dissected and attached to the bladder. The incisions are closed with sutures. A catheter may be left in place to drain urine from the bladder.
The complete surgery takes about 4 hours. You may have to stay in the hospital for 3 to 5 days, after the surgery. Like all surgical procedures, laparoscopic bladder augmentation may be associated with certain complications, which include:
- Bladder rupture
- Abdominal pain
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Need for open surgery
- Urinary incontinence (involuntary leakage of urine)
The advantages of laparoscopic bladder augmentation when compared to open bladder augmentation include:
- Smaller incisions and less scarring
- Faster recovery
- Less post-operative pain
- Reduced hospital stay